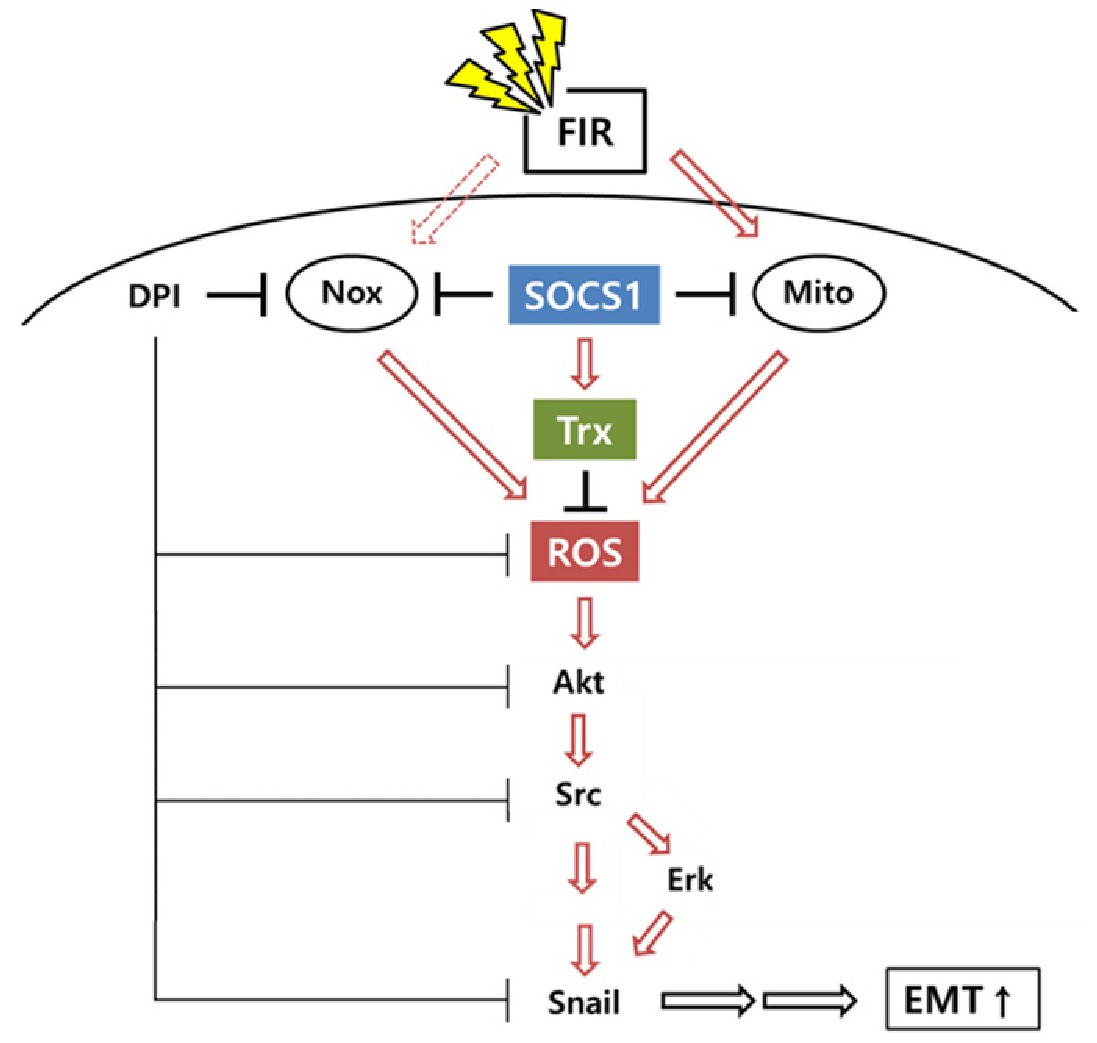
Fig. 8. A model for the FIR-induced ROS-mediated EMT signaling pathways and the inhibitory action of SOCS1 through the regulation of ROS-generating and ROS-scavenging systems. FIR triggers the induction of intracellular ROS derived from the action of Nox and functional mitochondria. ROS activates signaling pathways leading to EMT response through the Akt/Src/Erk pathways, resulting in increase in Snail with decrease in E-cadherin expression levels. SOCS1 suppresses ROS-mediated signaling through the induction of anti-oxidant factor Trx1 as well as through the down-regulation of Nox and mitochondria. The model depicts the critical role of ROS during the FIR therapy-induced EMT response and suggests the mechanism of anti-EMT function of SOCS1 by targeting both ROS-scavenging and ROS-generating systems to overcome the FIR-induced radioresistance associated with EMT.